World's Largest Iceberg, A23a, Threatens South Georgia's Delicate Ecosystem
The colossal iceberg A23a, currently the largest in existence, is on a potential collision course with the remote British territory of South Georgia.
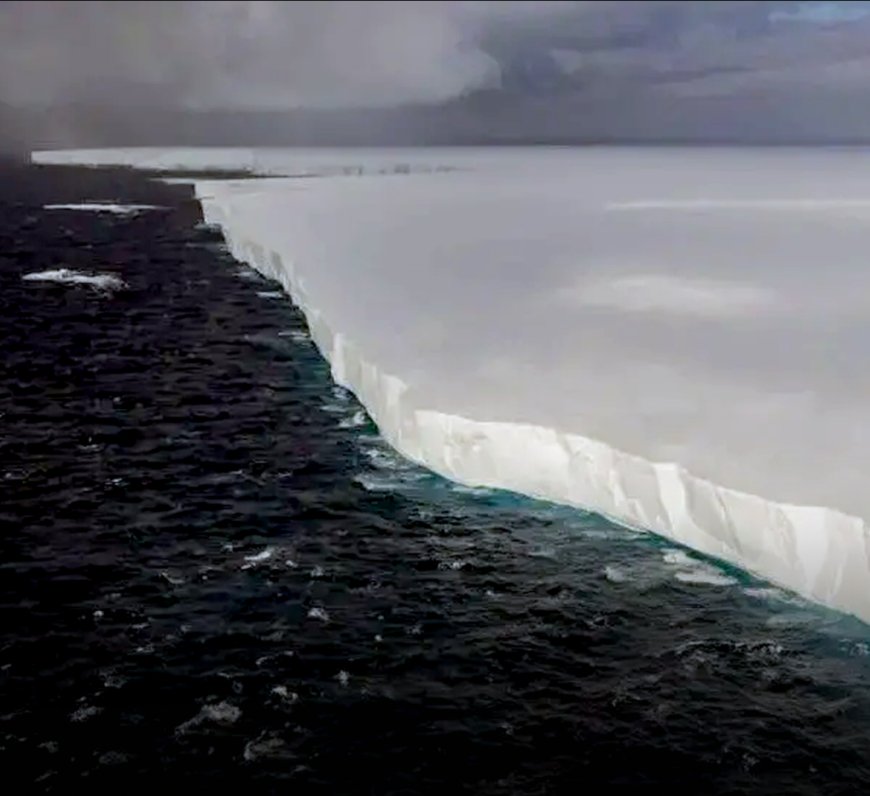

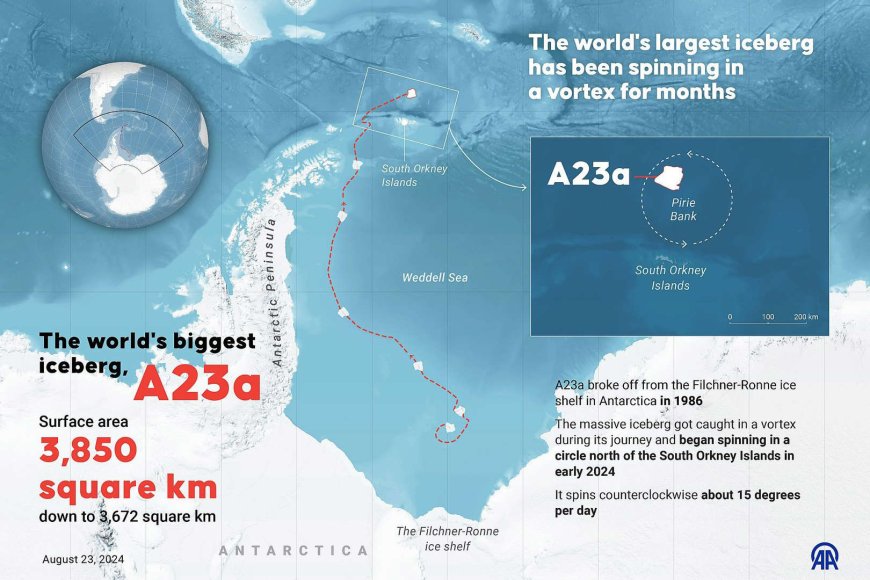
The colossal iceberg A23a, currently the largest in existence, is on a potential collision course with the remote British territory of South Georgia. This massive iceberg, which calved from Antarctica's Filchner–Ronne Ice Shelf in 1986, has been adrift for decades and now poses a significant threat to the island's unique wildlife and ecosystem.
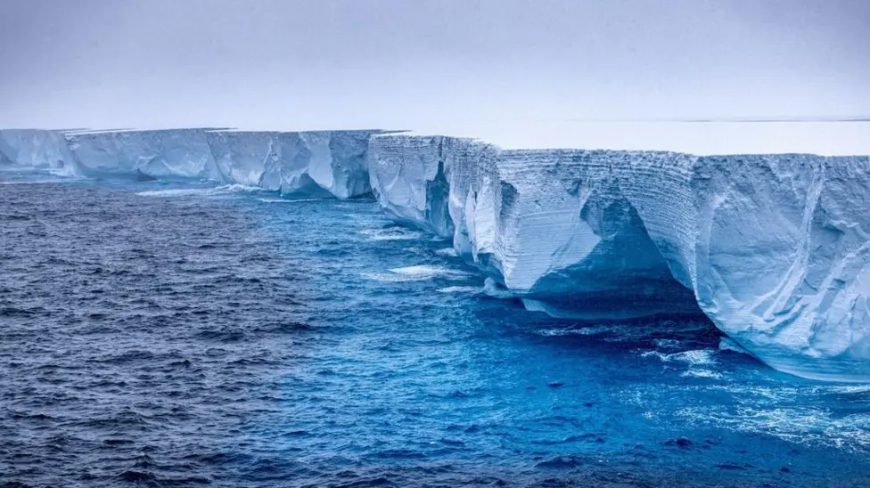

A23a: A Colossal Iceberg
Measuring approximately 3,500 square kilometers (1,400 square miles), A23a is comparable in size to the U.S. state of Rhode Island. Its dimensions are staggering, spanning several tens of kilometers in length and reaching depths of a few hundred meters. Despite its massive size, the iceberg has remained relatively intact since it broke free from the Antarctic ice shelf nearly four decades ago.
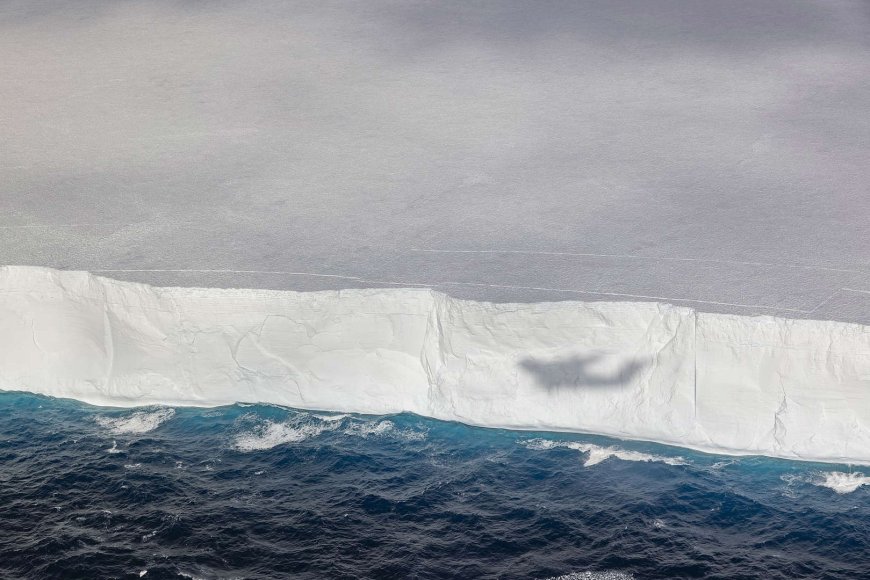

Journey Towards South Georgia
After calving in 1986, A23a remained grounded on the seabed of the Weddell Sea for over 30 years. In 2020, it began its slow drift northward, navigating the frigid waters of the Antarctic Ocean. As of January 2025, the iceberg is approximately 173 miles off the coast of South Georgia, following a path known to seafarers as "Iceberg Alley." Satellite imagery has been crucial in tracking its movement, revealing a gradual approach towards the island.
Potential Impact on South Georgia's Ecosystem
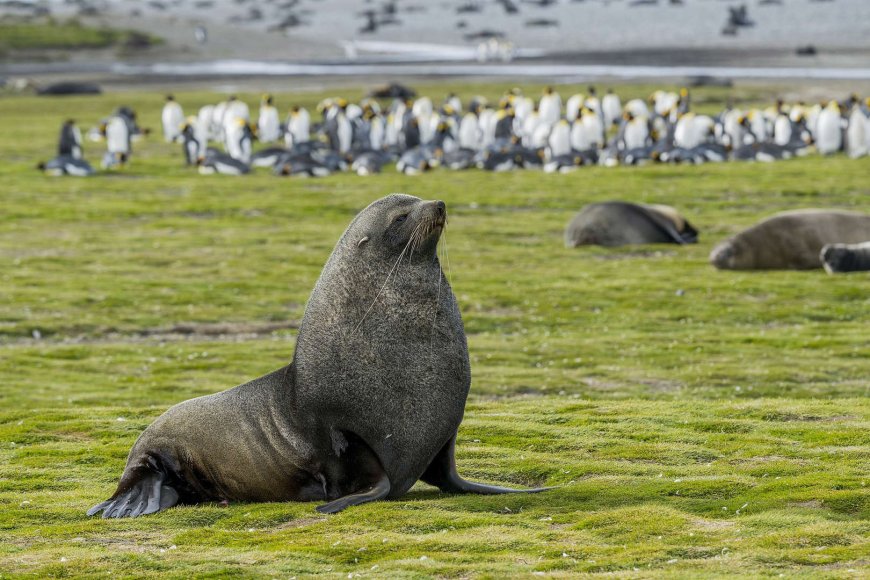
South Georgia is a haven for diverse wildlife, including various species of penguins, seals, and seabirds. The potential grounding of A23a near the island raises significant concerns:

-
Habitat Disruption: The massive iceberg could block access to critical feeding grounds for penguins and seals, especially during breeding seasons when food demand is high.
-
Marine Ecosystem Alteration: The presence of such a large ice mass could disrupt local ocean currents and water temperatures, affecting the availability of prey species and overall marine biodiversity.
-
Physical Destruction: If the iceberg were to collide with the island, it could cause physical damage to coastal and marine habitats, leading to long-term ecological consequences.
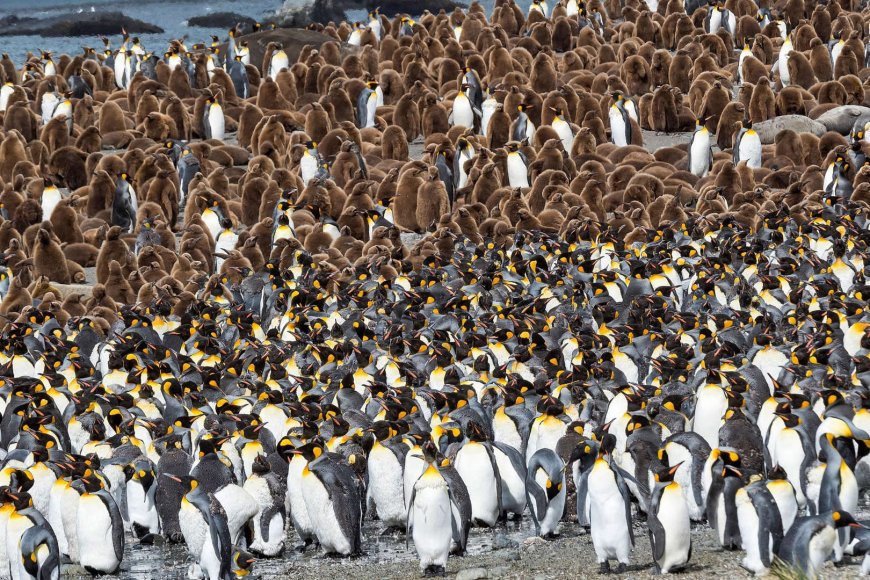

Historical precedents underscore these concerns. In 2004, the collision of iceberg A38 with South Georgia resulted in the death of numerous penguin chicks and seal pups due to disrupted access to feeding areas. More recently, in 2023, iceberg A76 narrowly missed the island, yet its proximity still posed threats to the local fauna.
Scientific Monitoring and Predictions
Researchers and scientists are closely monitoring A23a's trajectory using advanced satellite imagery and oceanographic data. Dr. Andrew Meijers, a physical oceanographer at the British Antarctic Survey, notes that the iceberg is currently in a meandering current, not moving directly towards South Georgia. However, prevailing currents suggest it may again move towards the island soon. The uncertainty of its path necessitates continuous observation to predict potential impacts accurately.
Global Implications of Iceberg Movements
The journey of A23a highlights broader environmental concerns:
-
Climate Change Indicators: The calving and movement of large icebergs are often linked to rising global temperatures, which accelerate ice shelf melting and destabilization.
-
Sea-Level Rise: While the melting of floating icebergs like A23a doesn't directly contribute to sea-level rise, their presence can influence the melting rates of adjacent land ice, indirectly affecting sea levels.
-
Ecosystem Vulnerability: The potential ecological disruptions caused by such icebergs underscore the fragility of polar and subpolar ecosystems in the face of environmental changes.
Conclusion
The looming presence of iceberg A23a near South Georgia serves as a stark reminder of the dynamic and interconnected nature of Earth's polar regions. As scientists continue to monitor its path, the situation underscores the importance of understanding and mitigating the broader impacts of climate change on vulnerable ecosystems worldwide.
What's Your Reaction?








































































































